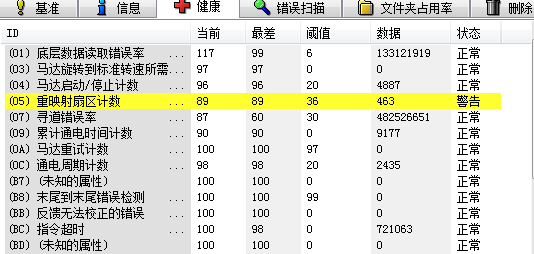
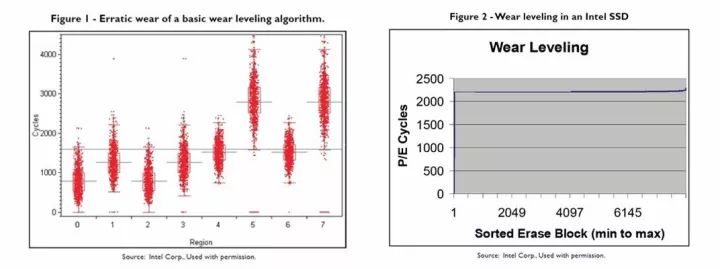
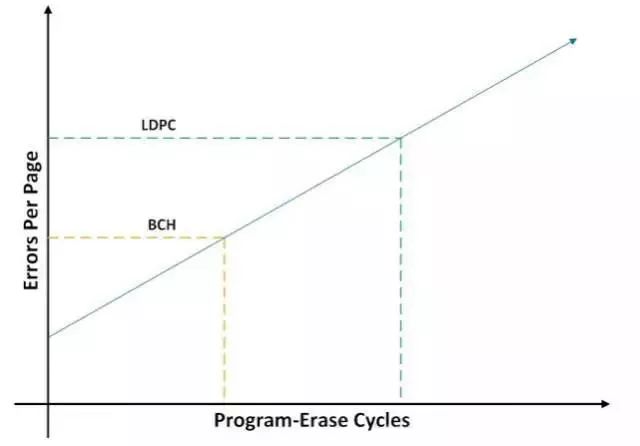
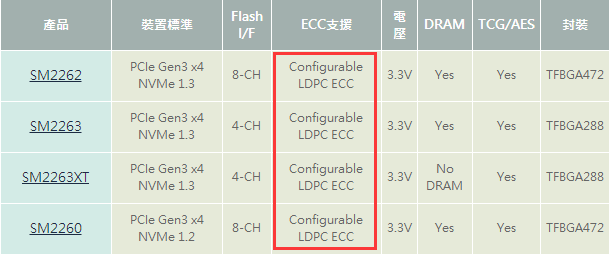
When it comes to SSDs, terms like MLC's 3000P/E and TLC's 1000P/E are commonly used to indicate the endurance of solid-state drives. These metrics play a vital role in determining how long an SSD can last under normal usage conditions. Beyond the inherent properties of the flash memory types, advanced algorithms also significantly contribute to extending the lifespan of SSDs. One of the most powerful tools in this regard is ECC (Error-Correcting Code) technology, which plays a critical role in maintaining data integrity and improving drive durability. The secret weapon for longer SSD life – ECC error correction As flash memory wears over time, errors can occur during data transmission or storage. These errors may lead to data corruption or system crashes if not properly addressed. This is where ECC becomes essential, as it helps detect and correct errors before they cause serious issues. However, even the best ECC systems have their limits. If the number of errors exceeds the correction capability of the controller, it can result in uncorrectable errors that affect performance and reduce the drive’s lifespan. For example, if a controller supports 12-bit ECC, but the flash requires 13 bits due to wear, the controller may no longer be able to correct those errors. This can lead to system downtime or data loss, especially when reading or writing to affected areas. In simpler terms, increasing the ECC capability from 12 to 20 bits can significantly boost the P/E cycle count. This means the SSD can endure more write operations, resulting in a longer overall lifespan without needing to replace the NAND flash itself. What are the different ECC error correction techniques? Early SSD controllers relied on BCH (Bose–Chaudhuri–Hocquenghem) error correction, which was effective but limited in scope. As technology evolved, more advanced methods like LDPC (Low-Density Parity-Check) became widely adopted. LDPC offers better error correction, allowing SSDs to maintain performance and reliability even as the flash wears out. With LDPC, the number of P/E cycles can increase from around 1000 to 1500, effectively boosting SSD endurance by up to 50%. This improvement doesn't require changing the NAND type, making it a cost-effective way to enhance drive longevity. While LDPC provides superior error correction, it also comes with higher power consumption and more complex hardware design. This often leads to increased costs, especially in high-end SSDs. For instance, Huirong Technology’s latest SSD controllers now support LDPC ECC, demonstrating the industry's shift toward more robust and reliable solutions. Minghao Solid-State Drives use the stable and reliable Huirong firmware, and new models now come equipped with LDPC ECC. This has significantly improved the lifespan of their SSDs. Looking ahead, as newer ECC technologies emerge, we can expect even greater improvements in both performance and durability. The future of SSDs looks bright—low-cost, durable, and high-capacity drives are just around the corner!
High
purity Tin wire is a special target material, Vacuum coating target technology
was used in Automobile glass.
Pure Tin Wire,Tin Wire,Tin Solder Wire,Tin Plated Copper Wire Shaoxing Tianlong Tin Materials Co.,Ltd. , https://www.tianlongspray.com


September 28, 2025