At present, software-defined networking (SDN) has become a fashionable topic in the industry. SDN technology and its possible impact have been highly valued by academia and industry. At the same time, there are different understandings and understandings of SDN. This article attempts to analyze the development context of SDN technology, analyze the connotation, essential characteristics, application fields, development trends of SDN technology, and then analyze the impact of SDN technology development. 1. "Different opinions" SDN At present, experts with a high degree of attention to SDN can be roughly divided into three categories: IDC design and operation and maintenance personnel, data equipment design and development personnel, and future network research and test personnel. These three types of experts focus on the starting point of SDN and have a different understanding of SDN, as well as different development visions and expectations of SDN. After the emergence of a new technology, various discussions such as tracing back to who the concept was first proposed, when it was proposed, and whether it was a new concept usually only have academic significance, and have no substantial help in understanding the nature of the new technology. Discussing the concept of SDN still needs to start with its real market demand. (1) SDN commercial demand first appeared in the data center In order to support the migration of virtual machines on the application server, the IDC internal network is usually a layer 2 network, because if a layer 3 network is used, the IP address of the application service corresponding to the virtual machine will change with the change of the virtual machine, bringing business Difficult to deploy and manage, and the layer 2 network does not have this problem. However, directly applying the existing Layer 2 network technology inside IDC will mainly bring about the following two problems: One is that in the Layer 2 network, in order to eliminate the loop of broadcast packets, the Spanning Tree (STP) protocol is usually used , A logical tree is constructed between network nodes, and traffic between nodes is transferred according to this "tree-like" topology. Even if there are multiple physical links between network nodes, only one link actually transfers data, and other links The roads are free (only for backup). However, within IDC, there are frequent data exchange requirements between multiple servers. The STP-based tree network topology cannot efficiently support this "horizontal" traffic. The idle links between servers also cause a large amount of network resources. Waste, so the STP-based Layer 2 network is too simple for IDC, and needs to be reformed, especially with the development of cloud computing, this kind of IDC internal layer 2 networking needs are more and more urgent. Another problem is that there are usually many application servers inside IDC, some reaching tens of thousands or even more than one hundred thousand. Layer 2 switches need to use ARP and other protocols to learn the source address of received packets to establish a MAC address table. There are many application servers, so there are also many MAC address entries, which usually exceed the capacity of the MAC address table of the conventional layer 2 switch, which results in a large number of MAC addresses that cannot enter the MAC address table. The layer 2 switch does not find the MAC in the MAC address table. The data frame corresponding to the address is broadcast in the Layer 2 domain, causing traffic flooding inside the Layer 2 network and affecting the internal network efficiency of IDC. The root cause of the above two problems is that the traditional layer 2 network design is too simple. The layer 2 switch will only learn the MAC address, and will not plan the data forwarding path based on the MAC address. That is to say, there is no one in the traditional layer 2 network. The control plane (or the control plane functions are very, very weak, and are integrated with the forwarding function), only the data plane (responsible for data frame forwarding). Therefore, it is an urgent need to increase the control plane (or strengthen the control plane function) in the Layer 2 network, and to be responsible for the traffic scheduling and management among the nodes in the larger Layer 2 network. The current mainstream solution is to use variants of the IS-IS routing protocol to build control plane routing functions; use Openflow to define the interface between the control plane and the forwarding plane. This leads to the concept that the control plane is separated from the forwarding plane. But this is only the separation of the control plane and the forwarding plane in the Layer 2 network. (2) SDN commercial demand comes from router internal function optimization In traditional routers, the interface between the control plane responsible for routing planning and routing strategies and the data plane responsible for data encapsulation and high-speed forwarding is not open and is tightly coupled together. Each manufacturer connects the control plane and the forwarding plane through its own protocol or interface, which is also the advantage of CISCO, JUNIPER and other advantageous manufacturers to maintain technical barriers and exclude emerging manufacturers. However, there are two forces that are quietly challenging this model: one is a large Internet company that has the need to build its own corporate network, and these Internet companies believe that the current communication needs of their own corporate network are specific, while traditional The functions of routers are too complicated, and more than 80% of the functions and features are not used in their own networks. However, when buying these routers, they have to pay for these useless functions. It feels more "injustice", so there is a self-design to achieve simplicity The demand for efficient routers is one of the original intentions of Facebook, Google, Yahoo and other companies to establish the ONF (Open Network Forum) and develop SDN standards. Because these Internet companies have a lot of successful experience in using their own customized application servers within IDC, they have good expectations for independent research and development of efficient routers. Another force is the emerging data equipment manufacturers, who try to form an open, standard device interface by breaking the tight coupling between the router ’s internal control plane and the data plane, so that the control functions can be centralized and separated separately. Forwarding equipment can be made more general and simple, and the cost can be made lower, which helps to break the monopoly position of manufacturers such as CISCO and JUNIPER. These manufacturers can obtain new development opportunities from it. Based on this consideration, the IETF carried out research on the separation of the internal control plane and forwarding plane of the router earlier, and established the FORCES working group to define the communication protocol between the internal control plane and the forwarding plane of the router. Although this also leads to the concept of separation of the control plane and the forwarding plane, this is the separation of the control plane and the forwarding plane in a three-layer network. (3) SDN commercial demand comes from future network research and experiment At present, in order to solve the problems of insufficient network address space, difficult service quality assurance, lack of security and trust mechanisms, and poor network management and control capabilities faced by IP networks, future network researchers actively study new network architectures and key technologies on the one hand, trying to solve these problems The problem is that although there are many research directions, a clear and consensus technical route has not been formed. On the other hand, when the technical route is unclear and new schemes are emerging, it is necessary to establish an ultra-large-scale experiment of future network new technologies. Verification environment (experimental network), on this experimental network to flexibly provide a resource-independent experimental environment for various technical solutions, thereby incubating preferred technologies. Countries such as the United States and Europe have established GENI and FIRE networks, respectively, for this purpose. During the construction of the test network, designers hope to be able to flexibly control and deploy routing protocols on the network nodes to achieve efficient forwarding. Therefore, there is an increasing demand for the separation of the control plane and the forwarding plane on the experimental network nodes. Through the separation of the control plane, the intelligence and concentration of the network control function, and the protocol-independent and high-efficiency of the network forwarding function can be achieved. In the case where the control plane and the forwarding plane are separated on the experimental network node, each time a new network architecture and solution appears, it can be designed and configured in the form of software on the implementation node to quickly implement the new network form, Efficiently support network technology innovation and verification. In addition to the above three SDN requirements and the corresponding three types of experts, some experts understand SDN as a unified intelligent network management, and are committed to achieving the purpose that a network management system can manage multiple network devices uniformly and intelligently, such as deployment in LTE In the design of IP RAN, an integrated network management system can be used to configure and manage multiple simplified edge routers to improve the efficiency of network strategy deployment. However, this understanding is to separate the management plane from the control plane and the data plane, not the separation of the control plane and the forwarding plane, and should not be understood as an SDN technology. 2. "Original Clear Source" SDN The above analyzes the three development needs of SDN. Taken together, these requirements are all pursuing the concept of "open" network. The opening of the network is an inevitable trend of industrial development. Not only can it bring high efficiency of the corresponding equipment and network, but it can further subdivide the industrial chain and bring new opportunities for industrial development. At that time, the "openness" between mechanical parts realized the standard interchange between parts, refined the industrial chain of mechanical processing, improved the production efficiency of finished machinery, and greatly promoted the development of the industrial revolution. In the field of network communications, similar expectations can be achieved through SDN technology. In the data device, it can be summarized into two planes, as shown in the following figure: To understand SDN from the perspective of network openness, we can divide SDN into three categories, and the openness between each category is an increasing relationship: Four Quadrant Dc Motor Controller 4 Quadrant Dc Motor,Four Quadrant Controller,4 Quadrant Dc Motor Controller,Four Quadrant Dc Motor Controller Jinan Keya Electron Science And Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.keyaservo.com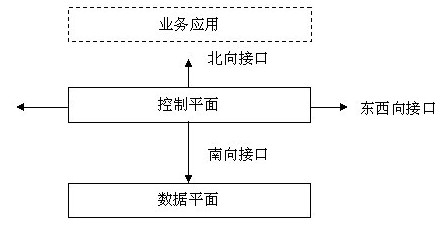
July 31, 2020