[Special] Preliminary investigation and research analysis of light intrusion in residential buildings
1 Introduction
The North American Lighting Engineering Association (IESNA) points out that non-essential light from indoors, that is, light intrusion, can cause discomfort, upset, or reduced visibility and distraction. "Environment and Health Outlook" magazine also pointed out that: nighttime outdoor light projection into the indoors will interfere with the secretion of hormones; outdoor lighting will disturb the minds of indoor people, people turn on the lights to get more light, indirectly affect people's activities . It can be seen that light intrusion may cause many harms to people: distracting attention, resetting the biological clock (the biological clock disorder is related to some diseases, such as depression, insomnia, cardiovascular disease and cancer), affecting the secretion of melatonin, etc. There is a direct interference effect with rest, so it is necessary to raise the hazard that emphasizes light intrusion.
In recent years, China's urban construction has developed rapidly and the nighttime light environment is relatively complicated. The problem of light intrusion in residential buildings in China is very serious. Light intrusion accounts for the largest proportion of light pollution in residential areas, and it is a kind of light pollution with high attention and the most difficult research in light environment research. This is due to the construction of commercial and service industries around the residential area, as well as the setting of lighting for roads, commercial plaques and advertisements. The forms of color light and dynamic flicker are also increasing, resulting in messy outdoor light entering the residential building and forming complex light intrusion. Environment (Figure 1). Residents' responses to this phenomenon are also different. The research results of international and domestic academic circles are less involved in this aspect. The relevant research results are few, and the feasible research methods are still unclear. The research potential of light intrusion It is imperative.

Figure 1. Different types and degrees of residential building light intrusion
This paper intends to analyze the current environmental characteristics of light intrusion based on the investigation status of intrusion light in Tianjin residential area, and to clarify the further trends and research contents of light intrusion research in residential buildings through the related research on light intrusion (light pollution).
1. Investigation of outdoor intrusion in residential areas
This part of the survey selects 47 residential areas newly built and under construction after 2000 in Tianjin's six districts, mainly using external testing and subjective survey methods. While recording the type of light source that generates intrusive light, in order to preliminarily evaluate the degree of light intrusion in the residential area, the degree of light intrusion in the investigated residential area is divided into no, low, medium, high, and serious according to the subjective feelings of the researcher and the situation of the field measurement. Level 5. The survey statistics are shown in Table 1. The purpose is to understand the source and influence degree of the intrusion light, and to prepare for the further investigation and to make basic preparations for measuring the light parameters of the intrusion light.
Table 1. Investigation of light intrusion in residential areas in Tianjin
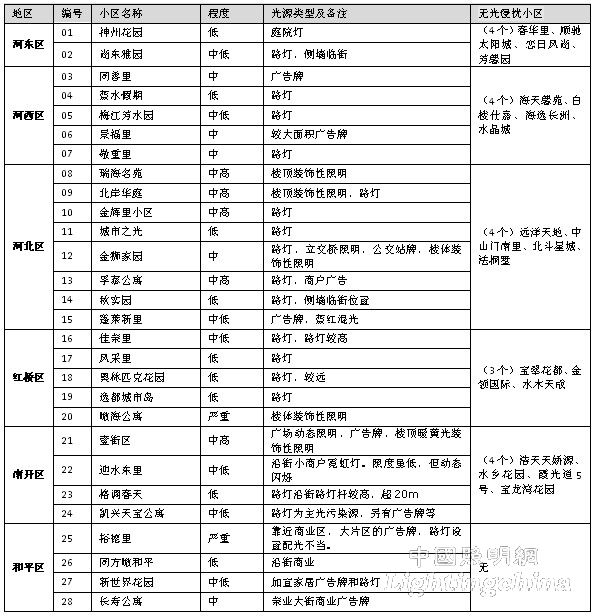
The data in the above table shows that 60% of the 47 residential communities have light intrusion, and the range is wide. Among them, moderate and high (including serious) accounted for 33% (Figure 2), and the impact of dynamic lighting also has a certain proportion. At the same time, it can be seen from the table that the source of intrusive light is complicated: street lights, neon lights along the street, signboards, bus stop signs, decorative lighting of buildings, large-area commercials, dynamic lighting (LED Display), etc. Composite sources accounted for 32%, of which 25% were from dynamic and color light sources (Figure 3).
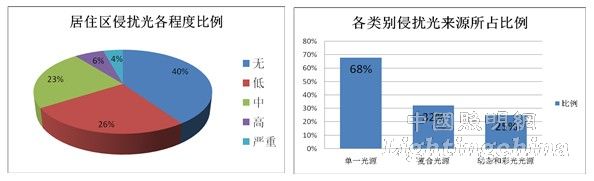
Figure 2. Light intrusion survey results
2 Existing research results and methods of light intrusion in residential areas
In the 1970s, there was a lot of discussion about urban light pollution in the field of international light environment research, mainly focusing on road glare and city night sky. In the past decade, the research on light pollution by European and American research institutions such as the International Commission on Illumination (CIE), International Dark Sky Association (IDA), IESNA, and some Asian research centers involved different types of land in cities such as night sky, commercial areas, and residential areas. The research results of different levels of roads and various types of interiors, including the intrusion of light in residential areas are summarized as follows:
CIENO.150, “Guidelines for Limiting the Effects of Interference Lights from Outdoor Lighting Facilities†(2003), states that the effect of lighting on occupants is usually related to the vertical illumination formed by the outdoor lighting rays entering the dark room on the window, and Dividing the lighting environment into four levels and two time periods, setting the standard requirements for the maximum allowable value of the vertical surface illumination generated by the outer surface of the living building window (see Table 2), and specifying the luminous intensity of the night lighting fixture toward the living room direction. Maximum allowable value.
Table 2. Maximum allowable values ​​for vertical illumination

IESNA's research includes the definition and measurement of light intrusion, and publishes "Lighting pollution:responses and remedies", "Light pollution: the global view", "Ecological Consequences of Artificial Night Lighting" and other works.
The "Outdoor site-lighting performance: A comprehensive and quantitative framework for assessing light pollution" published by the North American Lighting Research Center (LRC), describes the detection and calculation method of light pollution by OSP (Outdoor site-lighting performance), which is calculated by software simulation. The method of studying the light intrusion of residential buildings is a recent result of quantitative research on light intrusion. The OSP is based on the analysis of the measurement data of 125 regions (including the actual, experimental and software simulation). The calculation method is as follows: Firstly, the "cube" model surrounding the evaluation region space is established; then, The calculation of the light environment simulation software obtains the value of the measurement point on the cube; finally, the evaluation value of the light intrusion (the maximum value of the measurement point on the corresponding surface, unit lx) is obtained. "OSP is a system that can quantify the detection of light intrusion. The reflection of light intrusion from the 'point-type' thinking of the light source and the object being illuminated, to the 'three-dimensional' thinking mode of thinking about the two in one space," Refer to Figure 3.

Figure 3. Calculation model for the light intrusion of a double-sided pole, picture taken from "Lighting Pollution" P29
Japan's standards for the prevention and control of light pollution are also based on the limitations of CIE Technical Report No. 150.
China's light pollution research has also achieved some results in the past decade. It mainly focuses on research on the causes, hazards and control measures of light pollution based on the reality of the country or each city.
The Taiwan area has also conducted more research on the problem of light intrusion in residential buildings. Dr. Zhao Youchan of the National Cheng Kung University, "The Study of Outdoor Infrared Light Intrusion in Residential Areas" and Huang Guangyou's Master's Thesis "Study on the Intrusion of Street Advertising Lighting in Residential Areas" is based on outdoor street lighting and advertising intrusion in residential areas. Through investigation and actual measurement of the illumination of the residential window, the range of residential floors with light intrusion is investigated, and verified by software simulation, and suggestions for improvement and control measures are proposed to reduce the damage of the living environment from light.
In the article "Hazard, Trends and Prevention Strategies of Light Pollution" published by Xiao Huiqian and Hao Yunxu, the paper introduces the cases of light pollution hazards, and analyzes the research trends of international light pollution, and proposes the promotion of hazards to strengthen attention, survey and measurement. Summarize the prevention and control measures, strengthen the prevention and treatment standards and standardization, establish a supervision mechanism to do a good job in supervision and management. Lin Ruoci's "The Problem of Light Pollution in Urban Residences" quoted CIE No. 150 Technical Report, which explored the dangers and prevention of nighttime spills and stray light.
The "Cultural Ecology and Light Pollution Control" published by Yang Chunyu and others from Chongqing University pointed out that the ecological problems caused by light pollution caused by urban development should be paid attention to, and the specific methods of reducing light pollution from street street lights and other outdoor lighting facilities are proposed. The "Positive Pollution and Human Health" published by Wei Ming and Feng Hailiang of Chongqing University analyzed the causes of light pollution in cities and pointed out the hazards and prevention measures of light pollution.
The research results of Tianjin University are aimed at the living mode of residential areas in China, and systematically and quantitatively study the outdoor light environment indicators in residential areas. Su Xiaoming's doctoral thesis "Research on the Comprehensive Evaluation of Light Pollution in Residential Areas" established an evaluation formula for the degree of light intrusion in residential areas generated by road lighting:
T=32.285+0.002L-1.935S+2.719H-0.620D
Among them: T is the light infringement of residential buildings along the street (no unit)
L is the total luminous flux of the lamp (lm)
S is the distance between road and house (m)
D is the installation distance of the same side light pole (m)
H is the height of the pole (m)