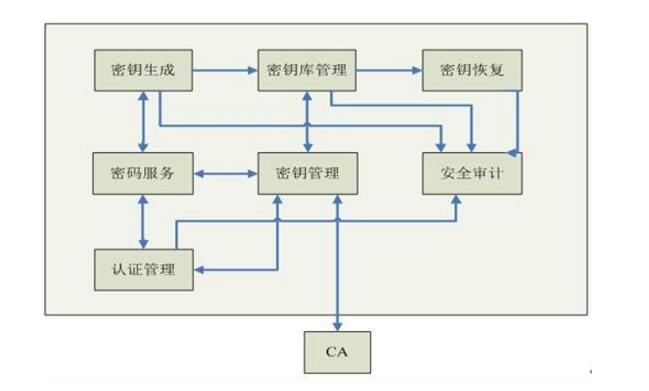
Introduction to the basic tasks and requirements of key management
**Introduction to Key Management**
A key, in the context of encryption, refers to a piece of information used to control cryptographic operations such as encryption, decryption, and authentication. It plays a critical role in protecting sensitive data, whether it's personal information or enterprise secrets. Key management involves the entire lifecycle of a key, from its creation to its secure destruction. This includes the development of key management systems, protocols, and processes for generating, distributing, replacing, and injecting keys.
In military computer network systems, where user mobility, affiliation, and coordinated command are complex, key management becomes even more crucial. Proper key management ensures that only authorized parties can access encrypted data and prevents unauthorized access or tampering.
**Types of Keys**
a) **Basic Key or Initial Key**: A basic key is selected by the user and allocated by the system. It may be assigned to a user for a long time and is also known as a user key. Together with a session key, it initiates and controls a key generator that produces a key stream for encrypting data.
b) **Session Key**: A session key is used between two communicating parties during a single session. It can act as a data encryption key when protecting transmitted data or as a file key when securing stored files. Session keys can be agreed upon by the parties or dynamically assigned by the system, making them also known as private keys.
c) **Key Encryption Key (KEK)**: This key is used to encrypt session or file keys during transmission across a communication network. Each node in the network typically has its own KEK.
d) **Host Master Key**: The Host Master Key is used to encrypt the Key Encryption Key and is stored within the host processor.
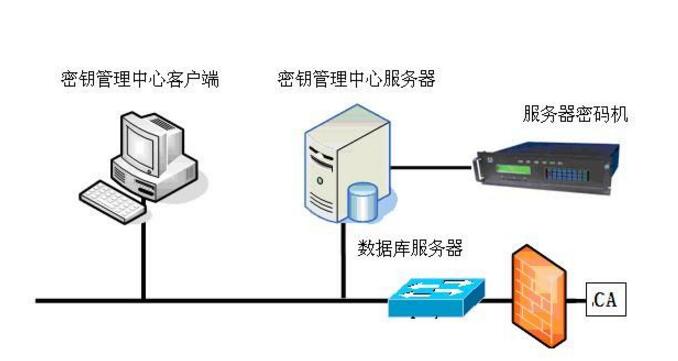
**Purpose and Scope of Key Management**
The purpose of key management is to standardize the confidentiality requirements for key usage in product development and production processes, ensuring that improper operations do not lead to information leaks.
**Scope of Application**
This regulation applies to the management of key usage in the company’s product design, development, and production processes.
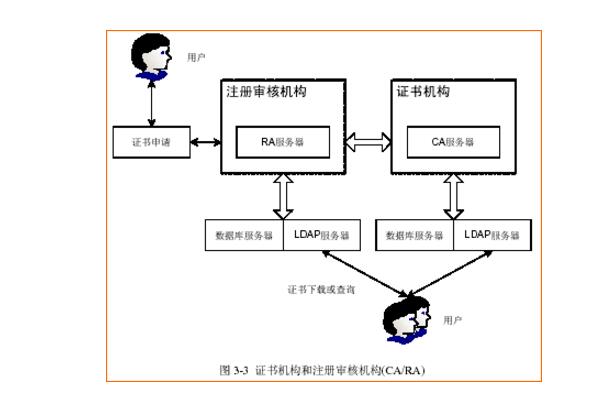
**Basic Tasks and Requirements of Key Management**
**1. Generation of Security Data**
Before personalization, appropriate encryption keys must be generated according to the specified procedures. At a minimum, the following keys should be created:
- **Issuer Master Key (KMC)**: Used to derive KMAC, KENC, and KDEK.
- *KMAC*: Locks the application area of China's financial IC card and verifies personalized data.
- *KENC*: Generates ciphertext for IC cards and verifies host ciphertext.
- *KDEK*: Encrypts confidential data written to the card during personalization.
- **Master Key (MDK)**: Used to export UDK for online card and issuer authentication. MDK is unique per BIN, while UDK is unique per card.
- **Issuer Public-Private Key Pair**: Generated by the issuing bank, with the public key sent to the certification body for a certificate, and the private key stored in HSM.
- **Key Exchange Key (KEK)**: Encrypts confidential data in the issuer's input file. Must be unique per issuer.
- **Transport Key (TK)**: Encrypts confidential data during transmission between the data preparation and personalization systems.
- **ICC Public-Private Key Pair**: Used for DDA and CDA/AC algorithms. The public key must be signed by the issuing bank's private key.
- **MDKENC**: Used to export UDKENC for encrypting the bank's script data.
- **MDKMAC**: Used to verify the bank's script data.
**2. Formation and Distribution of Keys**
Different encryption algorithms support different functions in the EMV Card Personalization Specification. However, incorrect implementation can compromise the intended security. Key management is essential for secure implementation.
For asymmetric keys like SM2/RSA, the security depends on protecting the private key. Risks include solving ECDLP or RSA modulus decomposition and private key leakage. To mitigate these risks, issuers should ensure strong key lengths, high-quality key generation, and secure storage.
When generating SM2/RSA keys, it is recommended to use a physically secure device with random number generators and tamper response mechanisms. Private keys should never be generated on untrusted devices.
Public keys should be securely transmitted via certificates or message authentication codes. Private keys must be protected during transfer using symmetric encryption and secure devices.
Symmetric keys are derived from master keys during personalization. They are used for specific transaction functions and must be managed carefully to prevent exposure.
**3. Preservation of Root Key Plaintext Data**
Root key plaintext data must be stored securely. Upon receiving key data, the manager must verify its integrity. If there is any doubt, the sender must be notified, and both parties must agree on the next steps. Hard copies should be stored in secure envelopes with logs of all access.
**4. Storage of Other Key Data**
Keys stored outside the card or HSM must be under dual control. HSMs should have secure memory and hardware to prevent electromagnetic leakage. PC boards used for encryption should provide similar protection to HSMs.
**5. Personnel Management**
Key managers must be officially appointed and undergo strict confidentiality checks. They must not be temporary staff or consultants. Backup personnel should be trained similarly to ensure continuity. Key managers are responsible for secure storage, verification, and destruction of keys, as well as logging all key-related activities.
Key management is a critical component of an issuer's security protocol, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of cryptographic operations.
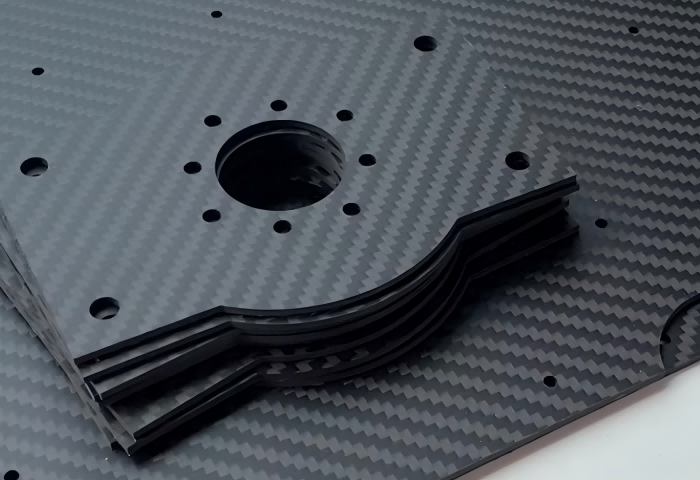
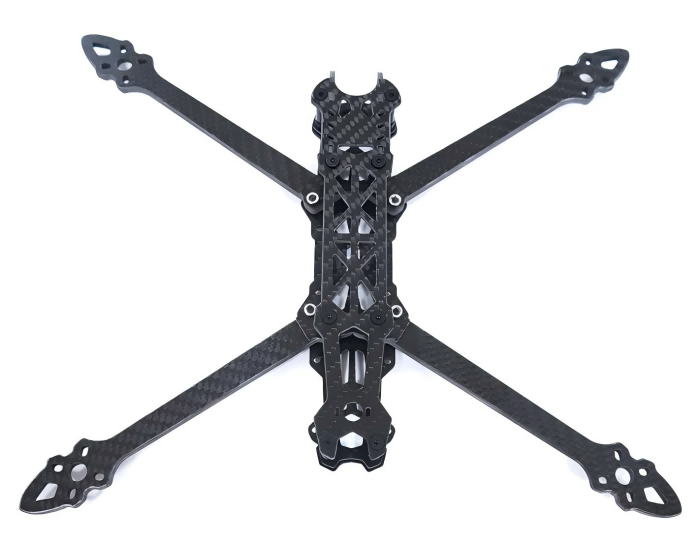
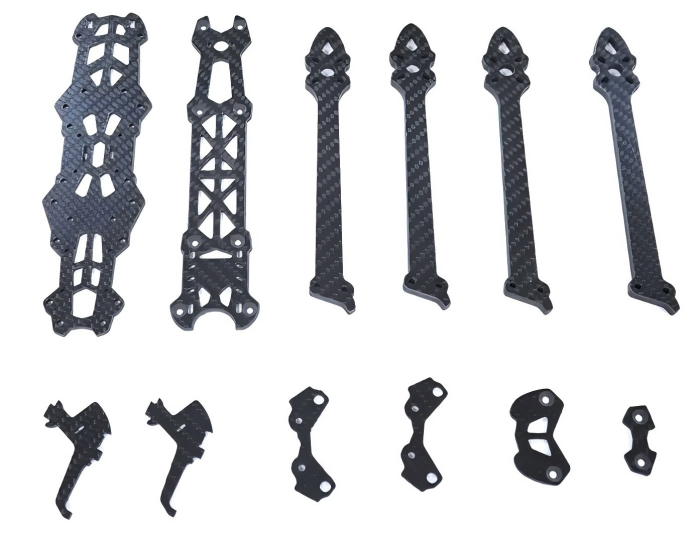



FPV Drone TrueX Frame Overview
Mark4 V2 Mark4 7inch 295mm / 8inch 367mm / 9inch 387mm / 10inch 427mm 3K Full Carbon Fiber TrueX Frame for FPV Camera Kit Done:
Mark4 V2 Mark4 7inch 295mm / 8inch 367mm / 9inch 387mm / 10inch 427mm 3K Full Carbon Fiber TrueX Frame for FPV Camera Kit Done:



Carbon Fiber FPV Drone Frame,FPV Drone TrueX Frame,Carbon Fiber FPV Frame
Jiangsu Yunbo Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.fmodel-ai.com