Cadillac draws high-precision maps to make self-driving taxis

On October 13, Netease Smart News reported that Cadillac has taken a bold step in the development of autonomous driving technology by integrating lidar sensors into its vehicles. Rather than just adding hardware to cars, the automaker is using advanced sensors to create detailed maps of U.S. and Canadian highways. These high-definition maps are then used to power Cadillac's semi-autonomous Super Cruise feature, allowing the vehicle to navigate complex roadways with minimal driver input.
This approach marks a significant shift in how autonomous vehicles are being introduced to the market. Full self-driving capability still depends on several factors, including government regulations, sensor advancements, powerful computing systems, and accurate mapping. As safety remains a top priority in vehicle laws, there's growing support for uniform federal guidelines rather than state-by-state variations.
As sensor costs continue to drop and their accuracy improves, the ability to process vast amounts of data becomes more efficient. High-resolution maps play a crucial role in enabling reliable navigation, whether on city streets or rural roads. Cadillac is leading the charge by deploying lidar-based maps, and while it may be the first, it won't be the last to follow suit.
Many modern vehicles with semi-autonomous features rely on map data to maintain their route. For example, Tesla uses crowd-sourced information, while Mercedes-Benz relies on Here maps to determine optimal speeds during turns. These maps are highly detailed, designed to support fully autonomous services like self-driving taxis.
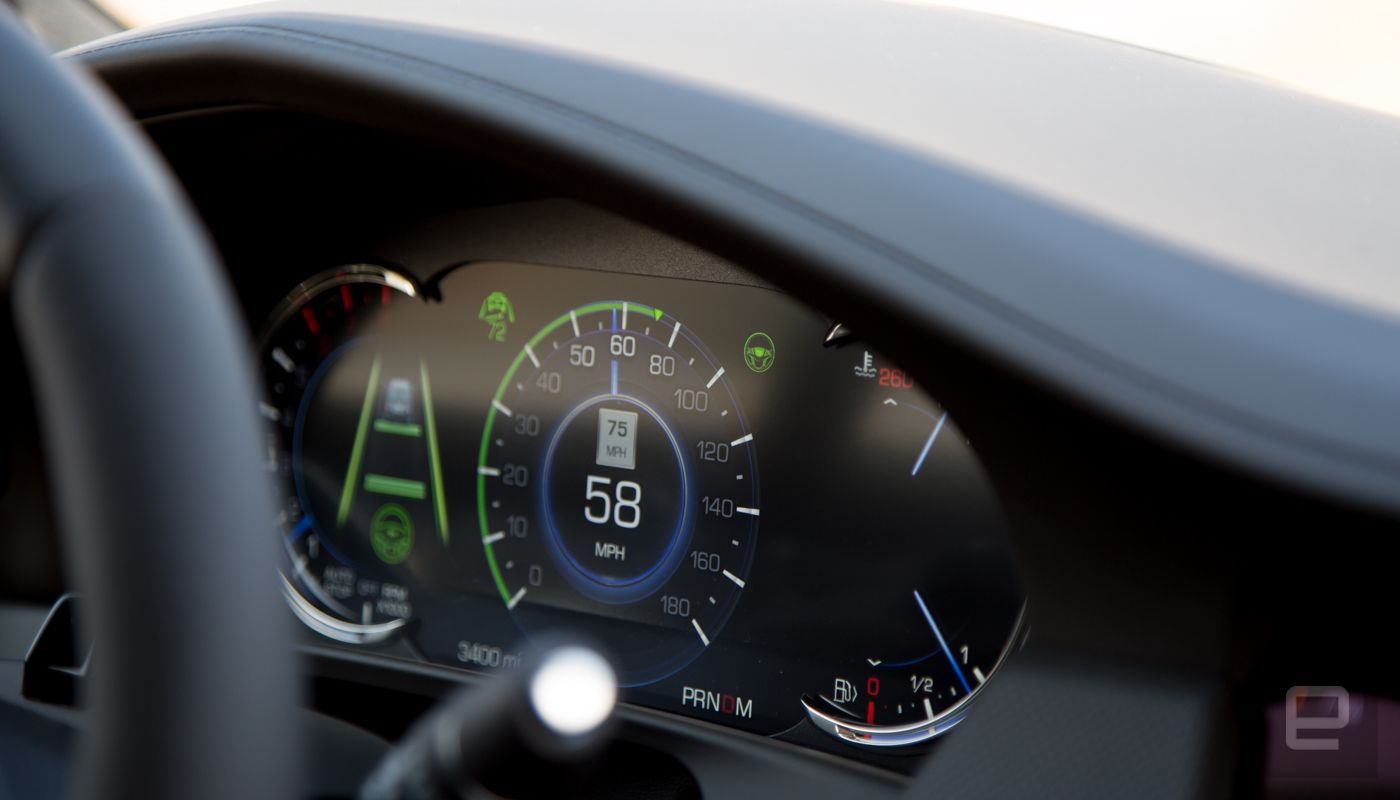
Cadillac’s Super Cruise system uses lidar maps stored in the trunk of the CT6 model, with an accuracy of within 10 cm. The system can scan up to 2,500 meters ahead of the car, providing real-time data to the onboard computer. This allows the vehicle to decide whether to continue in semi-autonomous mode or alert the driver to take control.
When companies like Uber and Lyft begin deploying self-driving taxis or autonomous bus fleets, they will need locally stored maps similar to those in the CT6. These maps must be updated frequently—sometimes every few seconds—to ensure seamless operation without relying on constant internet connectivity.

Even with advanced sensors and data, early self-driving taxis will operate along pre-defined routes to minimize risks. While they may slightly deviate to pick up passengers, if a vehicle is outside its designated area, users might need to walk a short distance to reach one. The underlying technology for autonomous vehicles is already advancing at the chip level.
Nvidia recently launched the Drive PX Pegasus, the world’s first AI-powered driving platform aimed at accelerating Level 5 autonomy. According to Danny Shapiro, Nvidia’s senior director of automotive, these vehicles will also generate and update maps as they drive. While this is part of the current development phase, it’s expected to evolve quickly.
In the future, thanks to innovations like Cadillac’s lidar technology, cars will be able to learn and adapt while driving. Enhanced sensors will collect more data, and more powerful computers will process it in real time. The level of detail in maps will grow exponentially, and as more manufacturers adopt this tech, all vehicles could make smarter decisions based on real-world experiences and simulations.
For now, Cadillac’s CT6 with lidar is helping bring self-driving capabilities to all types of roads, not just highways. However, in the early years, you might still have to walk a few blocks to find an autonomous taxi.
(Source: Engadget compilation; Netease Smart News - Robot Review: Rain Egg)
Follow the Netease Smart Public Account (smartman163) for the latest updates on artificial intelligence and tech trends.
Ic Logic,Logic Counters Dividers,Logic Fifos Memory,Logic Buffers Drivers Receivers Transceivers
Shenzhen Kaixuanye Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.icoilne.com